DAYANITHI G, 2001, INSERM U432, Montpellier, France.
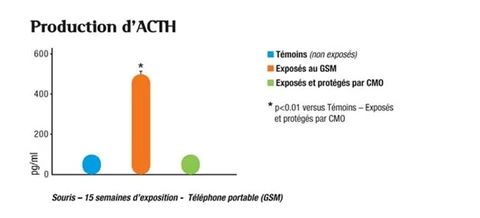
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic-cortico-tropic hormone) is a stress hormone. It is secreted by the adenohypophysis, according to the information received by the central nervous system. Its role is to stimulate the secretion of other hormones, especially cortisol (see below).
Abnormal changes in the blood levels of ACTH hormone and glucocorticoid (corticosterone, Cortisol) are symptomatic of a state of stress (ACTH = stress marker).
The increase of 300% in the rate of ACTH in animals under electromagnetic fields is an uncalled observation of the significant stress caused in its organism by the radiation of GSM (“electromagnetic stress”).
The presence of the compensating oscillator (CMO) allows to recover a normal rate of this hormone, an essential control of the regulation of the hormone-immune systems.


 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart. 
